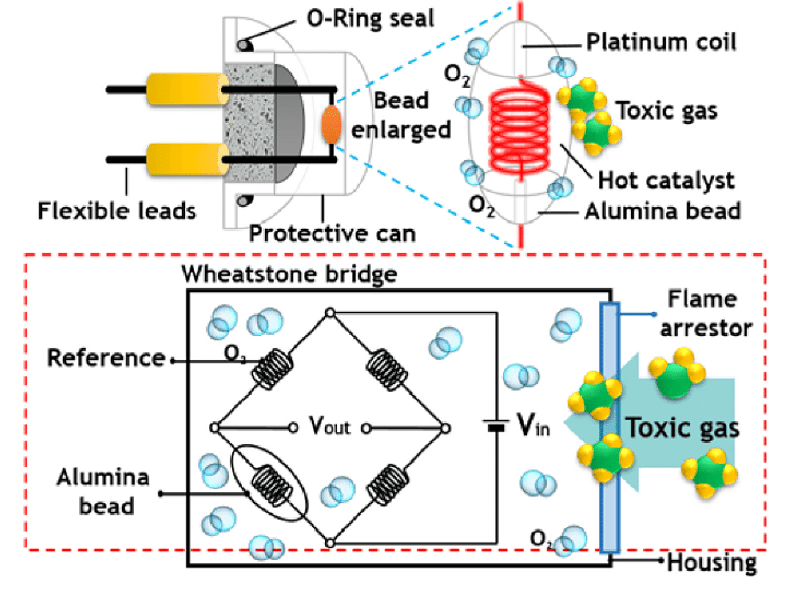
What are catalytic bead sensors? How do they work?
A catalytic bead sensor is a type of gas sensor commonly used in gas detectors. It works by detecting the presence and concentration of gases in the air using a chemical reaction. The sensor consists of a small bead coated with a catalyst, such as platinum or palladium, and a pair of electrodes.
When gas molecules come into contact with the catalyst on the bead, they react to form new chemical compounds. This reaction produces heat, which is measured by the electrodes. The amount of heat produced is proportional to the concentration of gas molecules present, allowing the gas detector to determine the concentration of the gas in the air.
The catalytic bead sensor is sensitive to a wide range of gases, including hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen sulfide. It is commonly used in industries such as mining, construction, and manufacturing to monitor the levels of potentially hazardous gases in the air and ensure the safety of workers.